Node.js and Ruby on Rails (RoR) are two popular server-side solutions for web application development. Despite the fact that both environments can manage apps of any complexity, they are built around different concepts and architectures.
As an app owner, you might be wondering which tool to choose for your next project. The choice might not be an easy one, but to make the final decision you should be aware of advantages and limitations of both Node and ROR, and, more importantly, understand cases and types of applications where Node.js may be better than Rails, and vice versa.
Interested in Ruby on Rails pros and cons? Read this article.
Node.js and Ruby Comparison
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime environment that features great native modules to deploy web servers, manage computing resources, file systems, and security of your applications. However, Node.js should not be confused with a web framework shipped with routers, controllers, database integrations and other handy tools to facilitate web development. Ruby and Ruby on Rails are much closer to that. It is quite a rich ecosystem consisting of small packages which, summed up, create solid web applications.
In a nutshell, Rails is a full-fledged web framework with a basic web development functionality provided out of the box. The framework is built on Ruby, a powerful and expressive programming language developed by Yukihiro Matsumoto in 1993.
Both RoR and Node.js are wildly popular among web developers. Rails is used by such popular sites and companies as GitHub, Shopify, Airbnb and SoundCloud, whereas Node.js is a preferred choice for PayPal, Uber, Netflix and other tech giants.
Pros of Node.js
1. Fast server-side solution
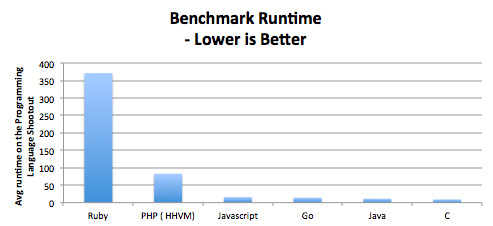
When we think about the strengths of Node.js, the first thing that comes to our mind is its innovative application of asynchronous and event-based programming and non-blocking I/O maximising the usage of a single CPU and computer memory. Thanks to this architecture, Node.js servers can process more concurrent requests than conventional multi-threaded servers. Node.js event loop, which does not block program execution under I/O-heavy workflow, improves runtime performance making Node one of the fastest server-side solutions around.
2. One language on both the front- and the back-end
Node.js is written in Javascript, a programming language that dominates front-end development. Some of the most popular front-end frameworks, such as Ember, React, and Angular, leverage power and flexibility of JS to create dynamic Web 2.0 applications. With Node.js installed server-side, developers can use the same programming language across the web stack. The same language at the front end and the back end means you need a smaller and more efficient team, which can communicate better and, as a result, deliver tasks much faster.
3. Scalable solution
Node.js is a very scalable solution too. Node clusters and workers are abstractions that can spawn additional Node.js processes depending on the workload of your web application. Limited only by the number of CPUs at their disposal, you can easily scale your Node applications to fully functional enterprise solutions.
Cons of Node.js
1. Less efficient with CPU intensive operations
At the same time, however, Node.js asynchronous and single-threaded models have certain limitations. Yes, Node is good at handling multiple concurrent events and requests. However, it is not as efficient when it comes to CPU intensive operations, such as generating graphics or resizing images. Luckily, a workaround of making a new task queue to manage CPU intensive requests exists, though it requires spawning additional workers, and introducing new layers to your Node.js application.
2. Poor quality or lack of documentations for some modules in npm
Also, Node’s flexibility may sometimes backfire on those who want to quickly deploy their web applications. The thing is that Node.js leaves it to the developer which modules to select. Although some choices may be obvious (e.g Express for a web server and routing), others may not. Developers might spend a considerable amount of time figuring out which library to choose for handling Javascript Promises (Async or, maybe, Bluebird), or which template engine to use. As result, more planning, time, and involvement may be needed to bootstrap a Node.js project. Developers have to find the right modules and follow instructions to integrate them. Some of these modules might be buggy and introduce unexpected behavior to your Node applications. Since a Node.js application may depend on dozens of modules, it is crucial to have an experienced developer in your team.
Pros of Ruby on Rails
1. Based on best web development practices
RoR creators describe Rails as an opinionated framework because it implements their vision of the best web development practices and solutions. Since RoR values convention over configuration, the framework ships with all necessary modules and libraries. All of them are implemented with MVC (Model-View-Controller) paradigm in mind.
2. Rich and well-developed infrastructure
Rails offers a fully integrated web server solution (Puma web server) and ActiveRecord database that allows to abstract schema and models. Even better, Rails features generators – powerful scripts that allow to rapidly scaffold a RoR application by creating the directory structure, files, controllers, routers, database models, and other common web development nuts and bolts. All this makes Rails suitable for rapid prototyping and deployment of web applications.
3. Easy portability across various database platforms
Similarly, web developer community values Rails for its easy portability across various database platforms. This feature is supported by the Rails database migrations. Active Model that underlies the Rails default database ActiveRecord can easily abstract the differences between various SQL back-ends. Rather than writing schema in pure SQL, migrations allow using easy Ruby DSL syntax to describe changes to tables. As a result, RoR allows creating a database-agnostic schema and models simplifying migration of Rails applications across different database environments.
Cons of Ruby on Rails
1. Less flexibility
If your application has unique functionality and demands, it may turn hard to adjust an opinionated framework such as Rails to your product’s needs. Since Rails imposes much of authority over the app development process, you may get to the point when adjusting the framework takes more time than building it from scratch, or using a less opinionated one.
2. Drop in performance
Since RoR offers a majority of modules out of the box, the framework is heavier and somewhat slower in performance than Node.js. It is also less efficient than Node.js in managing simultaneous requests. The only solution to this is using additional server instances, which consumes additional memory.
3. Slow Debugging
Rails large stack frames and multiple layers of abstraction can make a debugging of RoR applications difficult. Your development team has to spend more time fixing errors and making updates to applications. This may slow down development, testing, and production cycles.
So, How to Make the Right Choice?
Our brief overview demonstrates that neither Node nor Rails are perfect. If so, how to make the right decision about which one to use? The answer is straightforward: both environments are good for specific apps and tasks.
Node.js is more suitable for dynamic applications with multiple server requests, and frequent shuffling of data between the client and the server. What kind of applications are these? These are instant messaging apps like chats and collaborative apps (drawing, video conferencing) collectively referred to as RTAs (Real-Time Applications). Event-based Node.js architecture is perfect in handling heavy I/O operations, server requests and data flow in these apps. For the same reason, Node.js is a preferred choice for Single Page Applications (SPAs) that involve heavy client-side processing, rendering, and where the main function of the back-end is to provide a REST API. Similarly, whenever performance and scalability of web applications are of concern, lightweight and fast Node.js outperforms the Rails framework. That is why such companies as Linkedin began using Node.js for performance and scalability reasons.
Ruby on Rails, on the other hand, performs better than Node.js in CPU-intensive applications. Node.js is a single-threaded environment that was not designed for CPU intensive operations with graphics, images, and data. Making computations on vast arrays of data may simply block all incoming requests rendering the main advantage of the Node.js useless. If you consider building CPU-heavy applications, Rails is definitely a better option than Node. Rails is also better when the speed of development is critical. With all the modules and generators available out of the box, Rails is very powerful in Rapid Application Development (RAD). Just in few commands, you may have a fully functional prototype that may be amended with additional features later. Node.js repositories also provide generator scripts to speed up the development, but fast prototyping is the philosophy of Rails.
So, when choosing between Node and Rails you should consider a speed of development, performance, and scalability of your application, and the type of use cases it addresses. If your requirement is a fast development of CPU-heavy applications, go with Rails. On the opposite, choose Node.js if you are thinking about RTAs, SPAs, and other I/O heavy solutions. Hopefully, this overview will help you make the right choice of your web development environment for the next project.

Response to “Node.js vs Ruby on Rails Comparison - Which Environment to Choose for Your Next Project?”